AMERICA'S HISTORY
The ancient times of the Americas (North, South, and Central America, and the Caribbean) starts with individuals relocating to these spaces from Asia during the stature of the Ice Age. These gatherings are by and large accepted to have been secluded from individuals of the "Old World" until the happening to Europeans in the tenth century from Iceland drove by Leif Erikson and in 1492 with the journeys of Christopher Columbus.
The precursors of the present American Indigenous people groups were the Paleo-Indians; they were tracker finders who relocated into North America. The most mainstream hypothesis states that travelers went to the Americas using Beringia, the landmass presently covered by the sea waters of the Bering Strait. Little lithic stage people groups followed megafauna like buffalo, mammoth (presently terminated), and caribou, hence acquiring the cutting edge epithet "major game trackers." Groups of individuals may likewise have gone into North America on the rack or sheet ice along the northern Pacific coast.
Social attributes brought by the principal foreigners later advanced and produced such societies as Iroquois in North America and Pirahã of South America. These societies later formed into human advancements. As a rule, these societies extended sometime in the future than their Old World partners. Societies that might be considered progressed or socialized incorporate Norte Chico, Cahokia, Zapotec, Toltec, Olmec, Maya, Aztec, Chimor, Mixtec, Moche, Mississippian, Puebloan, Totonac, Teotihuacan, Huastec individuals, Purépecha, Izapa, Mazatec, Muisca, and the Inca.
After the journeys of Christopher Columbus in 1492, Spanish and later Portuguese, English, French, and Dutch pilgrim undertakings showed up in the New World, vanquishing and settling the found terrains, which prompted a change of the social and actual scene in the Americas. Spain colonized the greater part of the Americas from present-day Southwestern United States, Florida, and the Caribbean toward the southern tip of South America. Portugal got comfortable with what is for the most part present-day Brazil while England set up settlements on the Eastern bank of the United States, just as the North Pacific coast and in the majority of Canada. France got comfortable with Quebec and different pieces of Eastern Canada and guaranteed a region in what is today the focal United States. The Netherlands settled New Netherland (managerial focus New Amsterdam – presently New York), some Caribbean islands, and portions of Northern South America.
European colonization of the Americas prompted the ascent of new societies, developments, and at last states, which came about because of the combination of Native American and European customs, people groups, and establishments. The change of American societies through colonization is apparent in engineering, religion, gastronomy, expressions of the human experience, and especially dialects, the most boundless being Spanish (376 million speakers), English (348 million), and Portuguese (201 million). The pioneer period endured roughly three centuries, from the mid-sixteenth to the mid-nineteenth hundred years when Brazil and the bigger Hispanic American countries proclaimed autonomy. The United States got freedom from Great Britain significantly sooner, in 1776, while Canada framed a government domain in 1867 and got lawful autonomy in 1931. Others stayed connected to their European parent state until the finish of the nineteenth century, for example, Cuba and Puerto Rico which were connected to Spain until 1898. More modest domains, for example, Guyana got freedom during the twentieth century, while certain Caribbean islands and French Guiana remain part of a European capacity right up 'til the present time.
PRE COLONIZATION
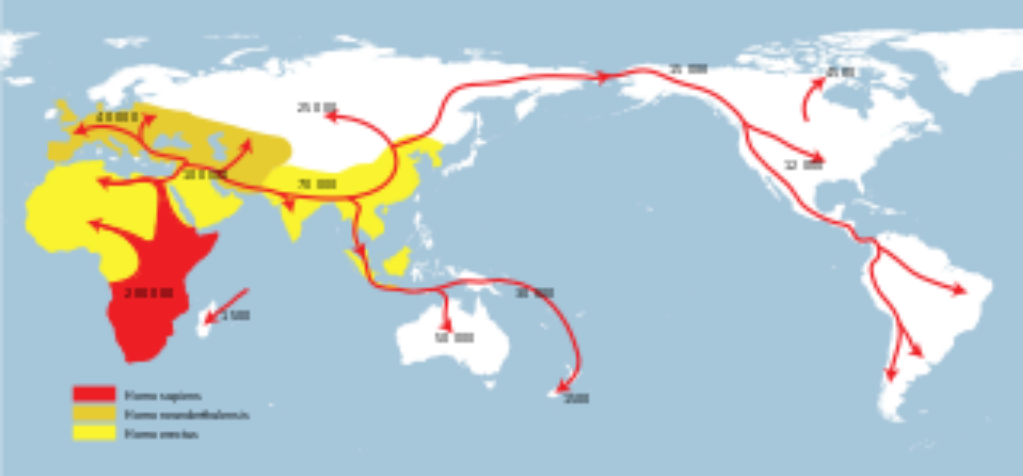
Migration into the continents
The points of interest of Paleo-Indian relocation to and all through the Americas, including the specific dates and courses voyaged, are dependent upon progressing research and discussion. When oceans levels were fundamentally brought due down to the Quaternary glaciation. These individuals are accepted to have followed groups of now-wiped-out Pleistocene megafauna along without ice hallways that extended between the Laurentide and Cordilleran ice sheets. Another course proposed is that, either by walking or utilizing crude boats, they moved down the Pacific Northwest coast to South America. Evidence of the last would since have been covered by an ocean level ascent of 100 meters following the last ice age.
Archeologists fight that the Paleo-Indian relocation out of Beringia (eastern Alaska), goes from 40,000 to around 16,500 years ago. This time range is a hot wellspring of discussion. A couple of arrangements accomplished to date are the beginning from Central Asia, with the far-reaching home of the Americas during the finish of the last icy time frame, or all the more explicitly what is known as the late chilly greatest, around 16,000 – 13,000 years before present. "Amerindian bunches in the Bering Strait area display maybe the most grounded DNA or mitochondrial DNA relations to Siberian people groups. The hereditary variety of Amerindian native gatherings increment with distance from the accepted section point into the Americas. Certain hereditary variety designs from West to East propose, especially in South America, that movement continued first down the west coast, and afterward continued eastward. Geneticists have differently assessed that people groups of Asia and the Americas were essential for a similar populace from 42,000 to 21,000 years ago.
New examinations shed light on the establishing populace of native Americans, recommending that their heritage followed to both east Asian and western Eurasians who moved to North America straightforwardly from Siberia. A recent report in the diary Nature revealed that DNA found in the 24,000-year-old remaining parts of a little youngster in Malta Siberia recommend that dependent upon 33% of the native Americans might have a lineage that can be followed back to western Eurasians, who might have "had a more north-easterly dissemination 24,000 years prior than regularly thought" Professor Kelly Graf said that "Our discoveries are critical at two levels. Paleoindian skeletons with phenotypic attributes abnormal for cutting edge Native Americans can be clarified as having a direct authentic association with Upper Paleolithic Siberia." A course through Beringia is viewed as more probable than the Solutrean hypothesis.
On October 3, 2014, the Oregon cave where the most seasoned DNA proof of human residence in North America was found was added to the National Register of Historic Places. The DNA, radiocarbon dated to 14,300 years prior, was found in fossilized human coprolites uncovered in the Paisley Five Mile Point Caves in south focal Oregon.
EUROPEAN COLONIZATION
Around 1000, the Vikings set up a fleeting settlement in Newfoundland, presently known as L'Anse aux Meadows. Hypotheses exist about other Old World disclosures of the New World, however, none of these are by and large or totally acknowledged by most researchers.
Spain supported a significant investigation drove by Italian voyager Christopher Columbus in 1492; it immediately prompted broad European colonization of the Americas. The Europeans brought Old World illnesses which are thought to have caused calamitous scourges and an immense diminishing of the local populace. Columbus came at a time in which numerous specialized improvements in cruising procedures and correspondence made it conceivable to report his journeys effectively and to spread the expression of them all through Europe. It was likewise a period of developing strict, royal, and financial contentions that prompted a rivalry for the foundation of provinces.







0 Comments